If you are working on Deep Learning or Machine Learning in general, you have heard of these three functions quite frequently. We know that they can all be used as activation functions in neural networks. But what are these functions and why do people use for example ReLU in this part, sigmoid in another part and so on? Here is a friendly introduction to these functions and a brief explanation of when to use which.
ReLU is a simple model which gives 0 value to all W*x + b < 0. The importance is that it introduces to our network the non-linearity, which is important for activations.
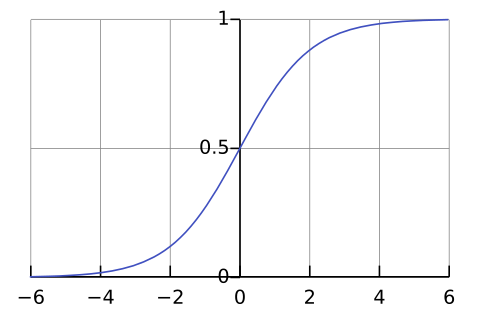
Sigmoid function
- Output from 0 to 1
- Exponential computation (hence, slow)
- Is usually used for binary classification (when output is 0 or 1)
- Almost never used (e.g., tanh is a better option)
Tanh function
- A rescaled logistic sigmoid function (center at 0)
- Exponential computation
- Works better than sigmoid
ReLU function (Rectified Linear Unit) and its variants
- Faster to compute
- Often used as default for activation function in hidden layers
ReLU is a simple model which gives 0 value to all W*x + b < 0. The importance is that it introduces to our network the non-linearity, which is important for activations.

Comments
Post a Comment